DataFrame Blog 1
Unit 1 – Data Handling I
DataFrames:
Data Frame is a 2-dimensional labeled data structure with columns of potentially different data types.
You can think of it like a spreadsheet or SQL table, or a dict of Series objects.
It is generally the most commonly used pandas object.
Like Series, Data Frame accepts many different kinds of input:
✔ dictionary of Series,
✔ list of dictionaries,
✔ Text/CSV files
❖ Dict of 1D ndarrays,
❖ Lists
❖ Series
❖ 2-D numpy.ndarray
❖ Another DataFrame
Along with the data, you can optionally pass index (row labels) and columns (column labels) arguments to the DataFrame construct.
If you pass an index and / or columns, you are guaranteeing the index and / or columns of the resulting DataFrame.
** When the data is a dict, and columns are not specified, the DataFrame columns will be ordered by the dict’s insertion order. Like a spreadsheet or SQL table, or a dict of Series objects.
When this table is created through the DataFrame( ) construct.
This is how the dataframe appears
** The row index by default is added to the table automatically as the very first column and the row indexing does not start with the column heading but rather with the first record onwards.
1. Creation of a Data Frame & 2. Display of a Data Frame
pandas.DataFrame(data_object ) – is the method which is used create a 2-D table from the specified data_object as an argument and the size of this table is mutable.
Steps to create a dataframe using the construct pandas.DataFrame( ) is
Step 1 Call the pandas library (by import statement)
Step 2 Define / Create the data_object
Step 3 Create the dataframe (by calling the DataFrame( ) constructor of pandas)
Step 4 Perform the Operation on the dataframe
I. Creating an Empty Data Frame
Step 1 Call the pandas library (by import statement)
as DataFrame( ) is a construct/method/function defined within the pandas library so, the code to call the library is
import pandas OR import pandas as <object_name>
Step 2 Define a dictionary of Series (Dos) / dicts (dictionary variable)
Ooops!!!! I don’t have a supply of any dictionary of Series
Step 3 Create the dataframe by calling the DataFrame( ) constructor of pandas and assign to a variable
import pandas
Mydf1 = pandas.DataFrame( ) # Calling DataFrame( ) constructor of pandas to create a
dataframe direct from library
OR
import pandas as pd
Mydf1 = pd.DataFrame( ) # Calling DataFrame( ) constructor of pandas to create a
dataframe through object
Display a dataframe - print( dataframe_object) or dataframename_object
Step 4 Display the dataframe
import pandas
Mydf1 = pandas.DataFrame( )
print(Mydf1)
2D - DataFrame 1
0 1 2
0 Aman 90 99
1 Naman 80 85
2 Yuvi 75 70import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
array1 = np.array(["Aman",90,99], index=[1,2,3])
array2 = np.array(["Naman",80,85], index=[1,2,3])
array3 = np.array(["Yuvi",75,70], index=[)
df1 = pd.DataFrame([array1, array2, array3])
print("2D - DataFrame 1 \n")
print(df1)dos_variable_name= { 'series1': pandas.Series( array of list ) , 'series2':pandas.Series( array of list ) ...}
Eg - Mydos={ 'Series1': pandas.Series( [10, 20, 30, 40, 50 ] ), 'Series2':pandas.Series( [ 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 ] ) }
Mydos={ 'Name':pd.Series(["Aman", "Naman","Celin"] ),
'Sub1':pd.Series( [90,80,70] ),
'Sub2':pd.Series( [95,85,86] ),
'Elec1':pd.Series([96,82,96]),
'Elec2':pd.Series([98,99,98])}
dFrameVI = pd.DataFrame(Mydos)
dFrameVI.index=[1,2,3]
dFrameVI.index.name="Roll No"
dFrameVI
Code to create dictionary of series with the given values is -
Series 1 Values
90
100
90
99
Series 2 Values
80
90
85
99
So let's do in steps -->
Step 1 🡪 import pandas as pd
Step 2 🡪 MyDoS = { 'Series1': pd.Series([90, 100, 90, 99]),
'Series2': pd.Series([80, 90, 85, 99])
}
Step 3 🡪 Mydf=pd.DataFrame(MyDoS)
Step 4 🡪 print(Mydf)
Let's see the output
Eg - 2 Code to create a dataframe from the given dictionary of series (with the given row index value)
Series 1 Values Index Address
90 Abhishek
100 Amitej
90 Prakhar
99 Bhavya
Series 2 Values Index Address
80 Abhishek
90 Amitej
85 Prakhar
99 Bhavya
Use the index argument of the pandas.Series( ) to label the index with the desired value instead of the default index address values 0, 1, 2, ...........
Step 1 🡪 <'Series_object_variable'>:pd.Series([90, 100, 90, 99], index=['Abhishek', 'Amitej',
'Prakhar', 'Bhavya’])
The above code will create a dataframe of a single series value and we have to create dictionary of Series
<'Series_object_variable'>: pd.Series([80, 90, 85, 99], index=['Abhishek', 'Amitej',
'Prakhar', 'Bhavya’])
Step 2 🡪 DictofSeries={ 'Series1': pd.Series([90, 100, 90, 99], index=['Abhishek', 'Amitej',
'Prakhar', 'Bhavya']),
'Series2': pd.Series([80, 90, 85, 99], index=['Abhishek', 'Amitej',
'Prakhar', 'Bhavya'])
}
After creating the dictionary of Series --> Create the dataframe
Step 3 🡪 Create the dataframe from DoS !!!!
Mydf=pandas.DataFrame(DictofSeries) # Using DataFrame( ) constructor of pandas
After creating the dataframe from DoS
Step 4 🡪 Display the dataframe
print( "The dataframe created from DoS" , Mydf)
# The program to create a dataframe from the given dictionary of series and to display is -
import pandas as pd
DictofSeries= { 'Series1': pd.Series([90, 100, 90, 99], index=['Abhishek', 'Amitej', 'Prakhar',
'Bhavya']),
'Series2': pd.Series([80, 90, 85, 99], index=['Abhishek', 'Amitej', 'Prakhar',
'Bhavya'])
}
Mydf=pd.DataFrame(DictofSeries)
print("\nDataframe from Dictionary of Series \n", Mydf)
What after creating a dataframe??????
You can perform certain operations on it like – Selection, Display, Iteration, Mathematical and statistical operations etc.
The row and column labels can be accessed respectively by accessing the index and columns arguments.
Eg 3 - Code to extract from a dataframe row wise or column wise
import pandas as pd
DictofSeries={ 'Series1': pd.Series([90, 100, 90, 99], index=['Abhishek', 'Amitej', 'Prakhar',
'Bhavya']),
'Series2': pd.Series([80, 90, 85, 99], index=['Abhishek', 'Amitej', 'Prakhar',
'Bhavya'])
}
Mydf=pd.DataFrame(DictofSeries)
print("\nDataframe from Dictionary of Series \n",Mydf)
Selective=pd.DataFrame(Mydf, index=['Prakhar', 'Bhavya', 'Amitej'], columns=['Series1', 'Series2'])
print("The new subset of dataframe by index and column is \n", Selective)
** The values assigned to index and column names in the argument should be same as mentioned in the dictionary os series.
Eg - 4 Code to extract a data / subset from a dataframe where a column name does not match / exist

In the above code when the dictionary of series is used to create a dataframe it has two columns Series1 and Series2.
Now, when the data from dataframe is filtered or extracted using row index and columns argument then the columns argument is given three values as
1. Series1 (which exists in dataframe)
2. Series2 (which exists in dataframe)
3. Term1 (which does not exist in dataframe)
In such a case where a column is extracted which actually does not exist in the main dataframe then the column will be dispalyed with the new column name as heading and the values will be NaN.
NaN - Not a Number, is the default value which appears as the cell value of a column of a dataframe which does not exist or has not been assigned with a numeric value or does not match with the values.
Eg - 5 Code to extract a data / subset from a dataframe where a column name does not match / exist
In the above code the row index 'Ananya' does not exist in the original dataframe. So in the extracted dataframe the column values for non matching row index 'Ananya' is shown with the default value NaN.
Creating a Data Frame using the data_objcect - from list of dictionaries
Mylod=[ {'Name':"Aman",'Sub1':90,'Sub2':95,'Elec1':96,'Elec2':98 },
{'Name':"Naman",'Sub1':80,'Sub2':85,'Elec1':82,'Elec2':99 },
{'Name':"Celin",'Sub1':70,'Sub2':86,'Elec1':96,'Elec2':98}
]
dFrameVII = pd.DataFrame(Mylod)
dFrameVII.index=[1,2,3]
dFrameVII.index.name="Roll No"
dFrameVII
Method 1 pandas.DataFrame(data_object ) – is the method which is used create a 2-D table from the specified data_object as an argument and the size of this table is mutable.
In order to create a dataframe you need to
Step 1 🡪 Call the pandas library (by import statement)
as dataframe is a module or a class defined within the pandas library.
import pandas OR import pandas as <object_name>
Step 2 🡪 Define a list of dictionaries
Ooops!!!! I don’t have a supply of any list of dictionaries
Step 3 🡪 Create the dataframe by calling the DataFrame( ) constructor of pandas and assign to a variable
import pandas
Mydf1 = pandas.DataFrame( ) # Calling DataFrame constructor of pandas to create a
dataframe direct from library
import pandas as pd
Mydf1 = pd.DataFrame( ) # Calling DataFrame constructor of pandas to create a dataframe through object
Step 4 🡪 Display the dataframe
import pandas
Mydf1 = pandas.DataFrame( )
print(Mydf1)

In the above code the list of dictionaries is not assigned to the dataframe and so the output is empty. The dataframe, index values, column values are all empty.
Now when the values of dictionaries are given
Dictionary 1 - { 'Abhisek' : 99, ' Amitej ' : 98, ' Aman ' : 99 }
Dictionary 2 - { 'Abhisek' : 96, ' Amitej ' : 99, ' Aman ' : 79 }
Then the list of such given dictionaries can be created by just enclosing these dictionary values in square brackets (as an array of list)
data_object = [ { dictionary 1}, {dictionry 2} , {.......... }, {........} ]
listofdict_variable = [ { 'Abhisek' : 99, ' Amitej ' : 98, ' Aman ' : 99 }, { 'Abhisek' : 96, ' Amitej ' : 99, ' Aman ' : 79 } ]
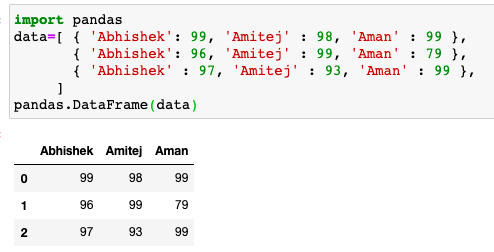
Eg - 2 Code to create and display a dataframe from the given list of dictionaries -
Eg - 3 Code to create and display a dataframe from the given list of dictionaries without the print statement
Eg - 4 Code to create a dataframe from list of dictionaries and display it with both the statements -
When print( ) is the second statement
In the above code the final output is in the format of print( )
When print( ) is the first statement
Eg - 5 Code to create and display a dataframe from a list of dictionaries where the column headings does not match in all the dictionaries.
In the above example the list is created of 4 dictionaries where each dictionary has its own set of column values (none of the dictionary keys are identical to each other). So in the output / display part the column(s) headings which does not match in the respective row has shown the default value NaN (Not a Number).
Eg - 6 Code to create and display a dataframe from a list of dictionaries with the changed row index values.
In the above example the default row index values have now been changed to subject names using index argument of the construct DataFrame( ).
Eg 7 - Code to create and dispaly a new dataframe created from a list of dictionaries with the changed row index values and also trying to show an extra row value which actually does not exist as an index value.
ValueError: Shape of passed values is (2, 3), indices imply (3, 3)2 rows and 3 columns are the actual dimension of the original data object (list of dictionaries)
3 rows and 3 columns are the desired dimesions of the new dataframe which has to be extracted from the original.
Dimension value mismatched. So, the output is a ValueError.
Method 2 pandas.DataFrame.from_dict(data_object , orient ) – is the method of DataFrame construct and not of pandas and is used to create a 2-D table from the specified data_object of type list of dictionaries.
orient is the argument which is supplied with either of the two values 'columns' or 'index'
The steps to create a dataframe from a list of dictionaries using the method / function pandas.DataFrame.from_dict( ) is same as of pandas.DataFrame( ).
Eg - 1 Code to create a dataframe using the from_dict( ) with the given values

In the above code the dataframe is created from a list of 2 dictionaries and displayed with the method from_dict( ) of the construct DataFrame.
And the dataframe which is created here with the method from_dict( ) is exactly the same in structure as when the dataframe was created with pandas.DataFrame( )
Eg - 2 Code to create and display a dataframe using the from_dict( ) with the given values where the columns (keys) are not matching in each row (dictionary)
In the above code the dataframe is created with the data object of type list of dictionaries and this list does not have matching keys in all the dictionaries. So, the unmatched keys (columns) have been shown with the default value NaN.
Sample reference program
Before we start with the argument orient let us once again have a look over the output of the dataframe created from a list of 3 dictionaries through from_dict( ) as in the above program.
Eg - 3 Code to create and display a dataframe created from a list of 3 dictionaries using the from_dict( ) with the argument orient and its value as columns
So, in the above code the argument orient is used and is assigned with the value column which in return has given the same output as the previous coding as Eg 2 without the argument orient.
Which means the default value of orient is column and it also mean that the dataframe which is made of list of dictionaries is oriented key wise (column) (Abhishek, Amitej are all keys)
Eg - 4 Code to create and display a dataframe created from a list of dictionaries using the from_dict( ) with the argument orient value as index
When the dataframe is created from a list of dictionaries and is oriented row wise (index wise) then the program returns an Attribute error because the list is an object which is of single dimension and that is why it fails to pick data row wise.
Display of the dataframe created from a list of dictionaries -
* with print( ) the dataframe is created but not stored any where and then displayed
* with print( ) as first statement the dataframe is shown in the normal format and with the direct statement of conversion / creation the dataframe is shown in a tabular structure.
* with print( ) as the second statement overwrites the display of the direct use of the statement and that is why the tabular structure is not shown.
Method 3 pandas.DataFrame.from_records(data_object, index, columns ) – is the method of DataFrame construct and not of pandas and is used to create a 2-D table from the specified data_object of type list of dictionaries.
index argument can be used to specify the alternative index value/ row name as a list of an array
columns argument is used to specify the columns or keys which should be extracted to show the dataframe. If such a column name is passed which is not a matching key in the dictionaries or does not exist in the dictionary then the values of such keys will be shown as NaN.
The creation of the dataframe is same as the previous two methods. Every output structure is also the same as of the above two methods.
Eg 1 -
Eg 2 -
Eg 3 -
*****************************************




























Comments
Post a Comment